Project 2622: N. Guil, R. Guidetti, M. Cesari, T. Marchioro, L. Rebecchi, A. Machordom. 2022. Molecular phylogenetics, speciation, and long distance dispersal in tardigrade evolution: A case study of the genus Milnesium. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 169:107401.
Specimen: Milnesium (unvouchered)
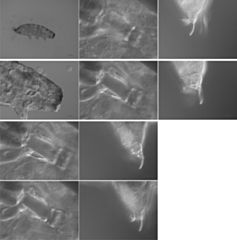
View: M437222 Habitus lateral view. Head lateral view. Lateral view buccopharyngeal apparatus in four different planes. Two planes of claws in PI in lateral view. Two planes of claws in PII in ventrolateral view.
View: M437222 Habitus lateral view. Head lateral view. Lateral view buccopharyngeal apparatus in four different planes. Two planes of claws in PI in lateral view. Two planes of claws in PII in ventrolateral view.
Abstract
Microorganisms (sensu lato, i.e., including micrometazoans) are thought to have cosmopolitan geographic distributions due to their theoretically unlimited dispersal capabilities, a consequence of their tiny size, population dynamics, and resistant forms. However, several molecular studies of microorganisms have identified biogeographic patterns indicating cryptic speciation and/or weak species definitions. Using a multi-locus approach with the genus Milnesium (Tardigrada), we aimed to determine the genetic structure of populations worldwide and the effects of long distance dispersal (LDD) on genetic connectivity and relationships across the six continents. Our results on this micrometazoan's genetic structure and LDD at global and micro-local scales indicate contrasting patterns not easily explained by a unique or simple phenomenon. Overall, we report three key findings: (i) confirmation of long distance dispersal for tardigrades, (ii) populations with globally-shared or endemic micro-local haplotypes, and (iii) a supported genetic structure instead of the homogeneous genetic distribution hypothesized for microorganisms with LDD capabilities. Moreover, incongruences between our morphological and molecular results suggest that species delimitation within the genus Milnesium could be problematic due to homoplasy. Duality found for Milnesium populations at the global scale, namely, a molecular phylogenetic structure mixed with widely distributed haplotypes (but without any apparent biogeographic structure), is similar to patterns observed for some unicellular, prokaryotic and eukaryotic, microorganisms. Factors influencing these patterns are discussed within an evolutionary framework.Read the article »
Article DOI: 10.1016/j.ympev.2022.107401
Project DOI: 10.7934/P2622, http://dx.doi.org/10.7934/P2622
| This project contains |
|---|
Download Project SDD File |
Currently Viewing:
MorphoBank Project 2622
MorphoBank Project 2622
- Creation Date:
21 February 2017 - Publication Date:
17 January 2022
Authors' Institutions ![]()
- University of Modena and Reggio Emilia
- Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales de Madrid (CSIC)
